How to Build a Custom yt-dlp GUI with Themes & MP3/MP4 Support
Creating a GUI Application to Download YouTube Media Using yt-dlp, Python, and FFmpeg
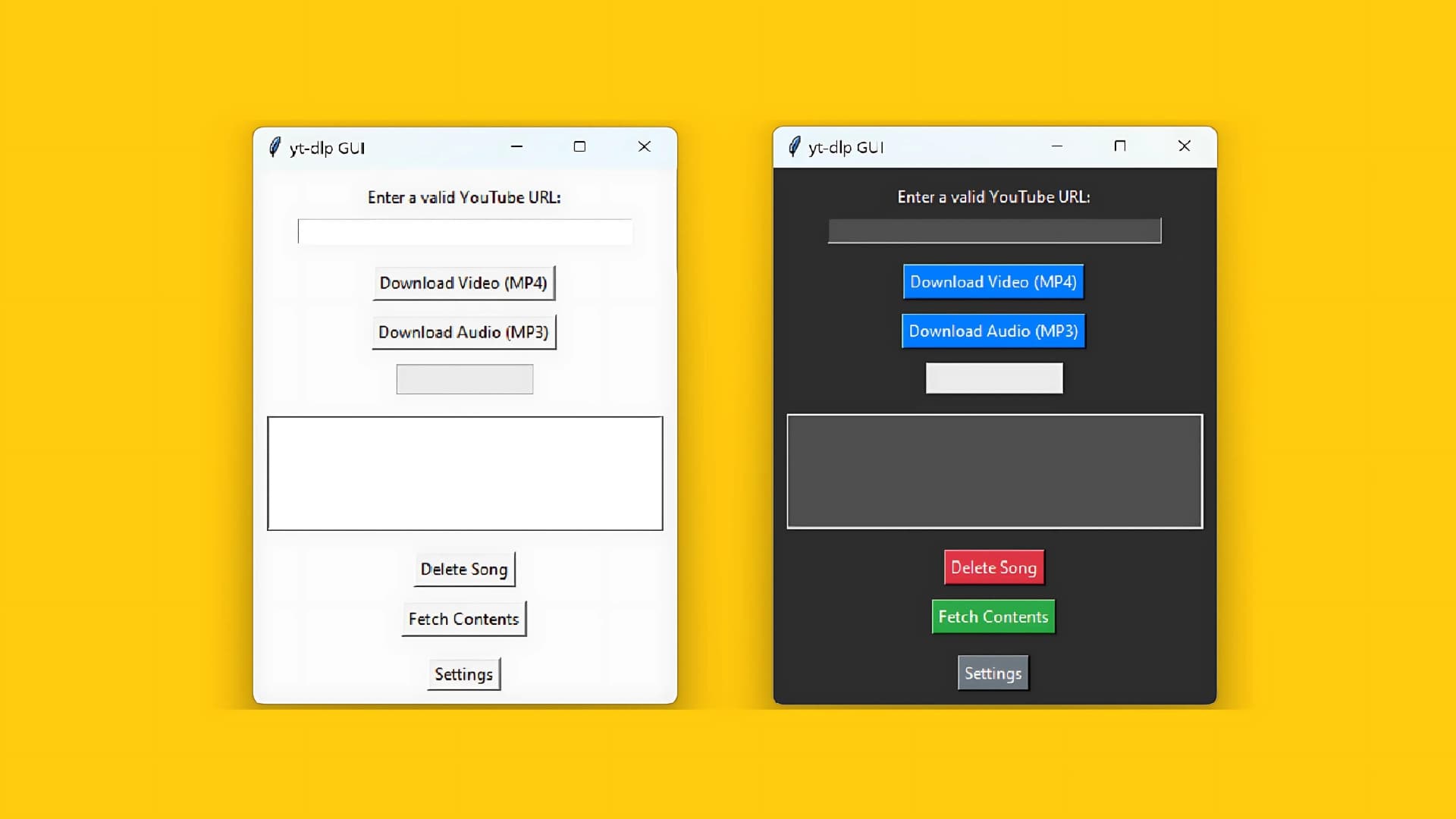
In this detailed guide, we'll create a Python GUI application for Windows that allows users to download media from YouTube using yt-dlp and convert it to either MP3 or MP4 format. The application will be built using the tkinter library for the GUI, and we'll use yt-dlp and ffmpeg for downloading and converting the videos.
The GUI will include a settings menu allowing users to switch from light to dark themes, as well as customize where the downloaded files are saved.
Download progress is shown in the progress bar, and the list of downloaded files is shown in the listbox where they can be deleted or opened.
advertisement
Before You Begin
-
Python: Ensure you have Python installed on your system. You can download it from the official Python website (https://www.python.org/).
-
yt-dlp: Install yt-dlp using pip:
pip install yt-dlp-
FFmpeg: Download and install FFmpeg from the official FFmpeg website (https://ffmpeg.org/download.html). Make sure to add FFmpeg to your system PATH.
a. Open System Properties:
-
Press
Win + Rto open the Run dialog. -
Type
sysdm.cpland press Enter. This opens the System Properties window.
b. Access Environment Variables:
-
In the System Properties window, click on the "Advanced" tab.
-
Click on the "Environment Variables..." button at the bottom.
c. Edit System Variables:
-
In the Environment Variables window, under "System Variables", find and select the Path variable.
-
Click on the "Edit..." button.
d. Add FFmpeg Path:
-
In the Edit Environment Variable window, click on 'New' to add a new entry.
-
Enter the path to the directory where you extracted FFmpeg. For example, if you extracted FFmpeg to
C:\ffmpeg, addC:\ffmpeg\binto the list. -
Click "OK" to close each window.
-
You may or may not need to perform a system restart. If the next step fails to return a version for ffmpeg, you can restart your machine and pick up where you left off (Step
ebelow).
e. Verify FFmpeg Installation:
-
Open a new Command Prompt window (
Win + R, typecmd, then Enter). -
Type
ffmpeg -versionand press Enter. -
You should see the FFmpeg version and configuration details printed in the Command Prompt if FFmpeg is correctly installed and added to the PATH. If you get an error, refer to step
d.4above.
-
-
tkinter: This comes pre-installed with Python. If not, you can install it using:
pip install tk- PyInstaller: Install PyInstaller using pip:
pip install pyinstallerStep-by-Step Guide
1. Setting Up the Project
Create a new directory for your project and navigate into it:
mkdir yt_downloader
cd yt_downloaderadvertisement
2. Writing the Script
Create a new Python file called main.py and open it in your favorite text editor. I recommend using VScode, but any editor will do. Place the following code into the file:
# main.py
import tkinter as tk
from settings import SettingsPage
from tkinter import filedialog, messagebox
from pathlib import Path
import yt_dlp
from tkinter import ttk
import configparser
import subprocess
class YoutubeDownloader:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("yt-dlp GUI")
# Load settings from the configuration file
self.load_settings()
# Default download folder
self.download_folder = Path(self.default_folder)
# Create the download folder if it doesn't exist
self.download_folder.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
# GUI elements
self.directions_label = tk.Label(root, text="Enter a valid YouTube URL:")
self.directions_label.pack(pady=(10, 0))
self.url_entry = tk.Entry(root, width=40)
self.url_entry.pack(pady=(5, 10))
self.download_button_mp4 = tk.Button(root, text="Download Video (MP4)", command=lambda: self.download_media('mp4'))
self.download_button_mp4.pack(pady=5)
self.download_button_mp3 = tk.Button(root, text="Download Audio (MP3)", command=lambda: self.download_media('mp3'))
self.download_button_mp3.pack(pady=5)
# Progress bar
self.progress = ttk.Progressbar(root, orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, length=100, mode='determinate')
self.progress.pack(pady=5)
# Listbox to display downloaded files
self.download_listbox = tk.Listbox(root, selectmode=tk.SINGLE, height=5, width=50)
self.download_listbox.pack(pady=10, padx=10)
# Bind the <<ListboxSelect>> event to a callback function
self.download_listbox.bind("<<ListboxSelect>>", self.on_listbox_select)
# Button for deleting songs
self.delete_button = tk.Button(root, text="Delete Song", command=self.delete_selected)
self.delete_button.pack(pady=5)
# Button for fetching contents
self.fetch_button = tk.Button(root, text="Fetch Contents", command=self.fetch_contents)
self.fetch_button.pack(pady=5)
# Settings button
self.settings_button = tk.Button(root, text="Settings", command=self.open_settings)
self.settings_button.pack(pady=10)
# Check if dark mode is enabled
if self.dark_mode:
self.apply_dark_mode()
# Load the list of downloads
self.load_downloads()
def apply_dark_mode(self):
# Apply dark mode color scheme to your widgets
self.root.configure(bg='#2C2C2C')
self.directions_label.configure(bg='#2C2C2C', fg='white')
self.url_entry.configure(bg='#4D4D4D', fg='white')
self.download_button_mp4.configure(bg='#007BFF', fg='white')
self.download_button_mp3.configure(bg='#007BFF', fg='white')
self.progress.configure(style='dark.Horizontal.TProgressbar')
self.download_listbox.configure(bg='#4D4D4D', fg='white')
self.delete_button.configure(bg='#DC3545', fg='white')
self.fetch_button.configure(bg='#28A745', fg='white')
self.settings_button.configure(bg='#6C757D', fg='white')
def load_settings(self):
# Load settings from the configuration file
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read("settings.ini")
# Update settings in the YoutubeDownloader instance
self.default_folder = config.get('Settings', 'DefaultFolder', fallback='yt-dlp-gui')
self.dark_mode = config.getboolean('Settings', 'DarkMode', fallback=False)
# Update the download folder based on the new settings
self.download_folder = Path(self.default_folder)
self.download_folder.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
def open_settings(self):
# Create an instance of the SettingsPage when the settings button is clicked
settings_root = tk.Toplevel(self.root)
settings_page = SettingsPage(settings_root, self)
def download_media(self, format):
url = self.url_entry.get()
if not url:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Please enter a YouTube URL.")
return
ydl_opts = {
'format': 'bestvideo+bestaudio/best',
'outtmpl': f'{self.download_folder}/%(title)s.%(ext)s',
'progress_hooks': [self.update_progress],
'cookies-from-browser': 'chrome' # Change to 'firefox', 'edge', or 'brave' if needed
}
if format == 'mp3':
ydl_opts['format'] = 'bestaudio/best'
ydl_opts['postprocessors'] = [{
'key': 'FFmpegExtractAudio',
'preferredcodec': 'mp3',
'preferredquality': '192',
}]
with yt_dlp.YoutubeDL(ydl_opts) as ydl:
try:
info_dict = ydl.extract_info(url, download=True)
title = info_dict.get('title', 'media')
messagebox.showinfo("Success", f"{format.upper()} download completed successfully.")
self.load_downloads()
except yt_dlp.DownloadError as e:
messagebox.showerror("Error", f"Download failed: {e}")
def update_progress(self, d):
if d['status'] == 'downloading':
# Update progress bar
progress_str = d['_percent_str'].strip('%')
try:
progress_value = float(progress_str)
self.progress['value'] = progress_value
self.progress.update_idletasks()
except ValueError:
pass # Ignore if the conversion to float fails
def load_downloads(self):
# Clear existing items
self.download_listbox.delete(0, tk.END)
# List all files in the download folder
for file in self.download_folder.iterdir():
if file.is_file():
self.download_listbox.insert(tk.END, file.name)
def delete_selected(self):
selected_index = self.download_listbox.curselection()
if selected_index:
selected_file = self.download_listbox.get(selected_index)
selected_path = self.download_folder / selected_file
# Ask for confirmation before deleting
confirm = messagebox.askyesno("Confirm Deletion", f"Do you want to delete {selected_file}?")
if confirm:
selected_path.unlink()
# Update the list of downloads
self.load_downloads()
def fetch_contents(self):
# Fetch contents of the download folder
self.load_downloads()
def on_listbox_select(self, event):
selected_index = self.download_listbox.curselection()
if selected_index:
selected_file = self.download_listbox.get(selected_index)
selected_path = self.download_folder / selected_file
# Open the file with the default media player
try:
subprocess.run([selected_path], shell=True)
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("Error", f"Failed to open file: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = YoutubeDownloader(root)
root.mainloop()advertisement
Then, in the same directory, create another Python file called settings.py and place this code inside:
# settings.py
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import filedialog
import configparser
class SettingsPage:
def __init__(self, root, youtube_downloader):
self.root = root
self.root.title("Settings")
self.root.geometry("400x200")
# Reference to the YoutubeDownloader instance
self.youtube_downloader = youtube_downloader
# Config file path
self.config_file = 'settings.ini'
# Dark mode checkbox
self.dark_mode_var = tk.BooleanVar()
self.dark_mode_var.set(self.youtube_downloader.dark_mode)
self.dark_mode_checkbox = tk.Checkbutton(root, text="Dark Mode", variable=self.dark_mode_var)
self.dark_mode_checkbox.pack(pady=10)
# Default download folder entry
self.default_folder_label = tk.Label(root, text="Default Download Folder:")
self.default_folder_label.pack(pady=(10, 0))
self.default_folder_entry = tk.Entry(root, width=30)
self.default_folder_entry.insert(0, self.youtube_downloader.default_folder)
self.default_folder_entry.pack(pady=5)
# Save button
self.save_button = tk.Button(root, text="Save", command=self.save_settings)
self.save_button.pack(pady=10)
# Load settings
self.load_settings()
def load_settings(self):
# Load settings from the configuration file
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read(self.config_file)
# Update GUI elements with the loaded settings
self.dark_mode_var.set(config.getboolean('Settings', 'DarkMode', fallback=False))
self.default_folder_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
self.default_folder_entry.insert(0, config.get('Settings', 'DefaultFolder', fallback='FM5'))
def save_settings(self):
# Save settings to the configuration file
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config['Settings'] = {
'DarkMode': str(self.dark_mode_var.get()),
'DefaultFolder': self.default_folder_entry.get(),
}
with open(self.config_file, 'w') as configfile:
config.write(configfile)
# Update the settings in the YoutubeDownloader instance
self.youtube_downloader.load_settings()
# Close the settings window
self.root.destroy()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = SettingsPage(root, None) # Pass None since we don't have a YoutubeDownloader instance in this context
root.mainloop()The will allow the user to select a theme (dark/light), as well as customize where the downloaded files are saved.
3. About the Code
-
Dependencies: The script uses tkinter for the GUI, yt-dlp for downloading videos, and ffmpeg for converting videos to audio.
-
Functions:
-
download_video: Downloads the video in MP4 format using
yt-dlp. -
download_audio: Downloads the video in the best audio format and then converts it to MP3 using
ffmpeg.
-
-
GUI Setup:
-
An input field for the YouTube URL.
-
Status bar indicating download progress.
-
Buttons to select between MP4 and MP3.
-
A button to start the download process.
-
A
settingsbutton for changing the app theme from light to dark, and well as customize where files are saved.
-
advertisement
FAQ
Do I need to install FFmpeg separately?
Yes, FFmpeg needs to be installed and added to your system PATH.
What if I encounter errors during the download process?
Ensure that the URL is correct and that you have a stable internet connection. Also, check that yt-dlp and ffmpeg are properly installed.
Can I download videos in other formats?
Yes, you can customize the ydl_opts in the script to specify different formats.
How can I add more features to this application?
You can enhance the GUI to include more options, such as selecting video quality, downloading subtitles, etc., by modifying the ydl_opts in the script.
How to Use:
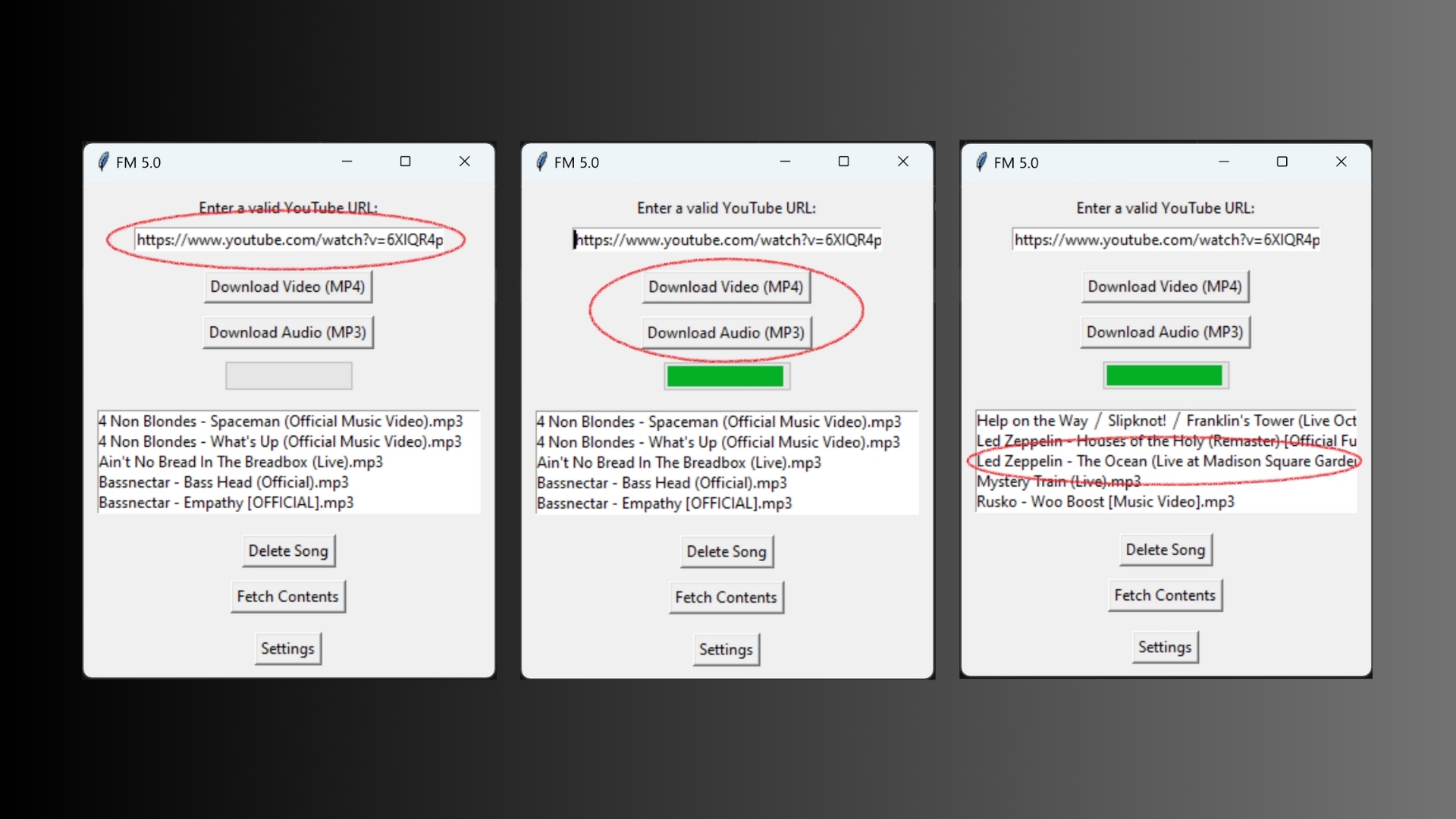
python main.pyEnter the URL of the YouTube video you want to download in the input field.
Select the format you want to download (MP4 or MP3).
Click the download button to start the download process.
Screenshots:
Related Articles
Useful Resources
-
Supported Sites: A full list of supported sites whose URLs can be used with yt-dlp for downloading can be found here (https://github.com/yt-dlp/yt-dlp/blob/master/supportedsites.md). This list includes a wide variety of video hosting and streaming platforms.
-
yt-dlp: For more information about yt-dlp, visit the official yt-dlp GitHub repository (https://github.com/yt-dlp/yt-dlp). This repository contains comprehensive documentation, installation instructions, and usage examples.
Donate
If you enjoyed this article, please consider making a donation. Your support means a lot to me.
- Cashapp: $hookerhillstudios
- Paypal: Paypal
Conclusion
In this guide, we've walked through the steps to create a YouTube downloader with a GUI using Python, yt-dlp, and ffmpeg. With this knowledge, you can further customize and expand the application to fit your needs.
advertisement
About the Author

Hi, I'm Jared Hooker, and I have been passionate about coding since I was 13 years old. My journey began with creating mods for iconic games like Morrowind and Rise of Nations, where I discovered the thrill of bringing my ideas to life through programming.
Over the years, my love for coding evolved, and I pursued a career in software development. Today, I am the founder of Hooker Hill Studios, where I specialize in web and mobile development. My goal is to help businesses and individuals transform their ideas into innovative digital products.
Read Recent Articles
Recent Articles
View All
CompressIt - Fast & Efficient Image Compression Tool for Web Optimization
December 02, 2024




to join the conversation